One highlight of the day was the keynote from Matt Parker; I have to confess to spending the first few minutes wondering why this bloke looked so familiar until I realised that I'd seen him in the superb Numberphile videos. He was highly entertaining, but also gave a few decent ideas for use in the classroom, such as thinking about images as RGB spreadsheets and creating a mega-Menger sponge or a fractal Christmas tree.
My three speed-dates were as follows:
- Catching up with a colleague from my old school - I know, this isn't really what speed dating is for, but we did have a good chat about their decisions regarding GCSEs and A Levels!
- Paul (@PaulRodrigo2718 ), who showed me his method for scaffolding problem-solving questions at GCSE.
- Richard (@TickTockMaths), who shared the absolutely superb dudamath.com, which I'd not seen before but has so much going on that its potential for use in the classroom seems massive.
Rather than attempting to blog about each workshop (I still haven't finished my #mathsconf7 round-up - now unlikely to ever happen!), I decided to make the most of my time off by doing a bit of relaxing colouring-in - so this conference's workshop posts are in "visual blog" format. I attended:
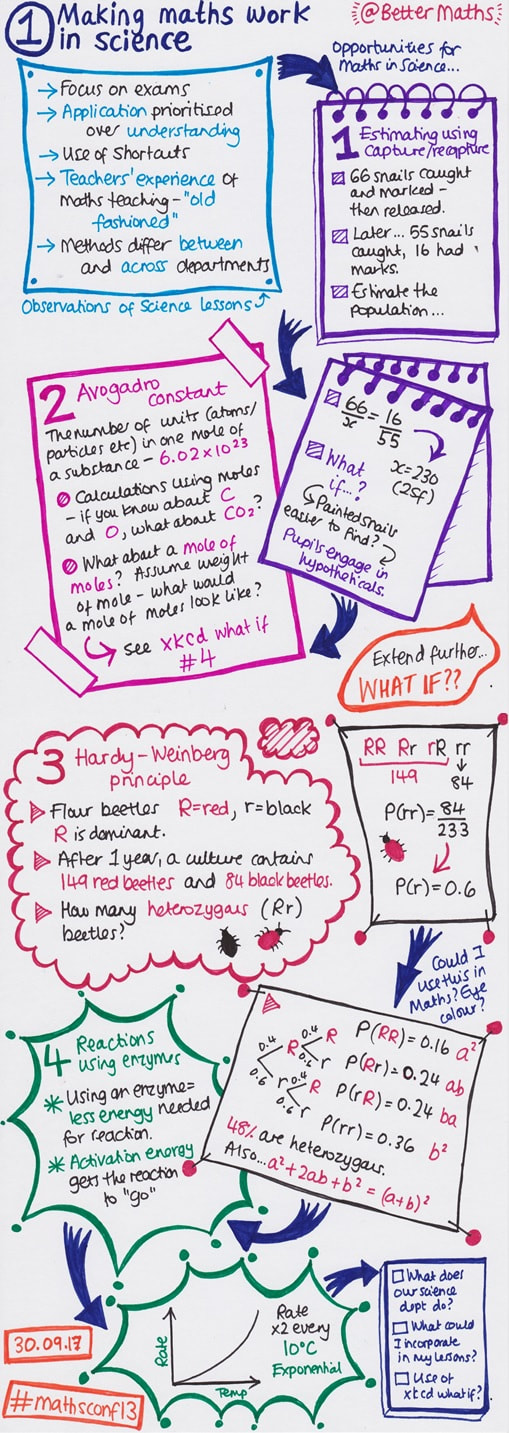
- Making Maths Work in Science with Luke Graham (@BetterMaths);
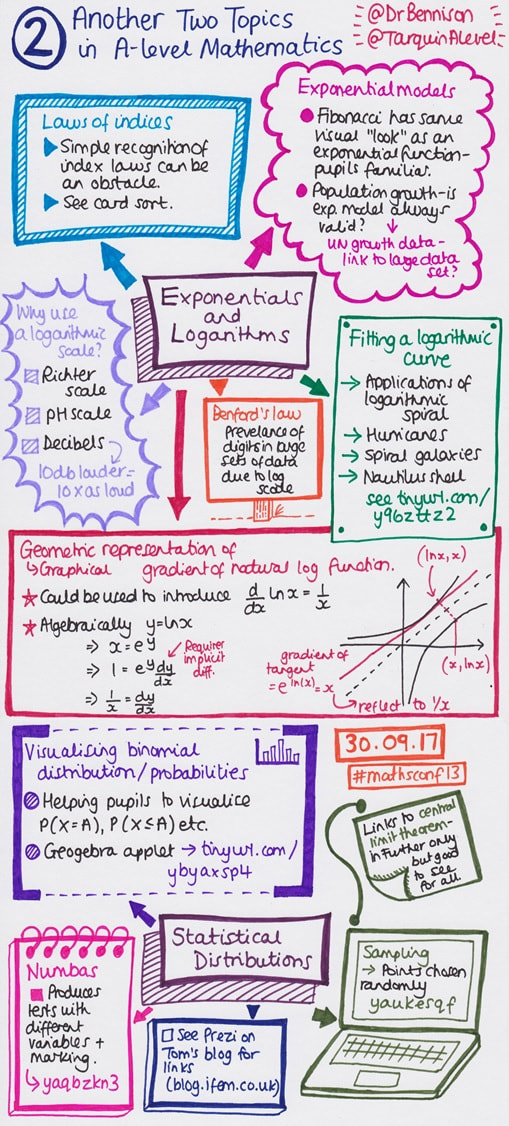
- Another Two Topics in A Level Mathematics with Tom Bennison (@DrBennison) and Ed Hall (@TarquinAlevel);
- Things to Do With your Large Data Set with Stella Dudzic;
- Problem Solving - Getting to Grips with the Overarching Theme 2 in the New Maths A-level with Dan Rogan.






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
